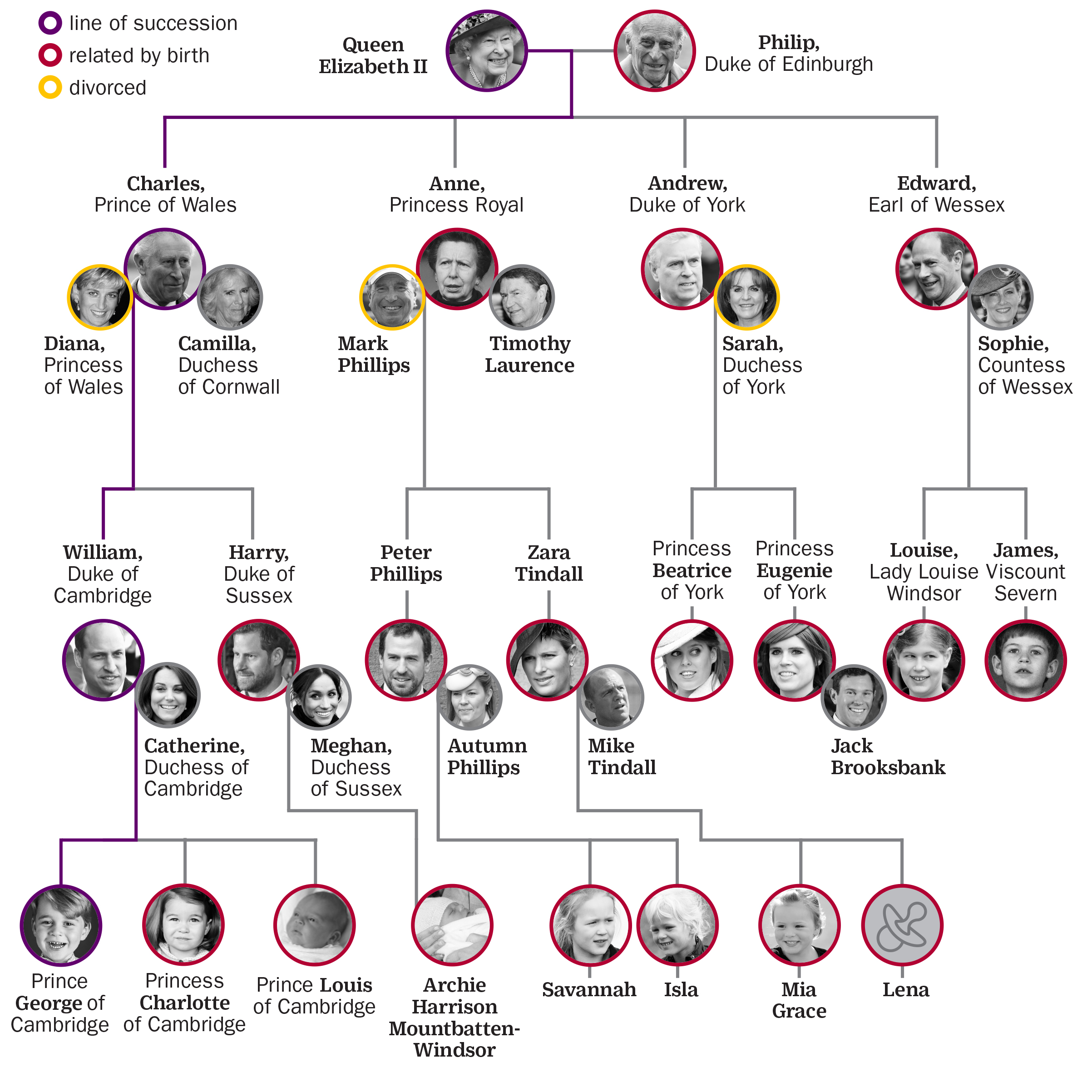
What Is Crown Family Succession? Unlocking The Secrets Behind Royal Lineages
Picture this: A royal palace, sparkling jewels, and a long line of family members waiting for their turn to wear the crown. But what exactly is crown family succession? It’s not just about passing a shiny tiara from one generation to the next—it’s a complex system with centuries of tradition, rules, and sometimes, drama. If you’ve ever wondered how royal families decide who gets the throne, you’re in the right place.
Crown family succession might sound like something out of a fairy tale, but it’s a real-life process that governs the future of monarchies around the world. From England to Japan, every royal family has its own set of rules for determining who inherits the throne. But why does it matter? Well, the way a monarchy transitions power can shape the future of entire nations.
So, buckle up because we’re about to dive deep into the world of crowns, thrones, and royal lineages. Whether you’re a history buff, a fan of royal dramas, or just curious about how these systems work, this article will give you all the answers you need—and maybe even spark a few debates along the way.
Table of Contents
- What is Crown Family Succession?
- History of Crown Family Succession
- Modern Rules of Succession
- Famous Succession Disputes
- Gender and Succession: The Evolution
- Religious Factors in Succession
- How Different Countries Handle Succession
- The Role of Parliament in Succession
- The Future of Crown Succession
- Conclusion: Why Crown Succession Still Matters Today
What is Crown Family Succession?
Let’s break it down real quick. Crown family succession is basically the process by which a royal family determines who gets to wear the crown next. It’s not as simple as saying, "Hey, oldest kid, you’re up!" There are rules—lots of them—and they vary depending on the country and the dynasty in question.
In most cases, succession is based on primogeniture, which means the firstborn child of the reigning monarch gets the throne. But here’s where things get interesting: not all countries follow the same rules. Some prioritize male heirs over females, while others have moved toward gender equality in succession. And then there are those pesky little details like religion, bloodlines, and even scandals that can mess everything up.
The Importance of Crown Succession
Why does crown family succession matter so much? Well, think about it: the monarch is often seen as a symbol of national unity and continuity. A smooth transition of power can strengthen public trust in the monarchy, while a messy one can lead to chaos—or even war. That’s why these rules are so carefully crafted and, in some cases, fiercely debated.
History of Crown Family Succession
Back in the day, crown family succession wasn’t always so… structured. In ancient times, kings would often just pick their favorite son—or whoever they thought could handle the job best. But as civilizations grew more complex, so did the rules. Enter primogeniture, which became the go-to method for ensuring a clear line of succession.
But even with primogeniture, things didn’t always go smoothly. Wars were fought, alliances were made, and sometimes, the wrong person ended up on the throne. Take the War of the Roses in England, for example. That whole mess was basically a family feud over who deserved to be king. Spoiler alert: it got ugly.
Key Moments in Crown Succession History
- The Magna Carta (1215): Limited the power of English kings and set the stage for future succession laws.
- The Act of Settlement (1701): Established the rules for British succession, including the requirement that monarchs must be Protestant.
- The Japanese Meiji Constitution (1889): Formalized the imperial succession process in Japan.
Modern Rules of Succession
Fast-forward to today, and crown family succession has become a lot more… civilized. Most countries with monarchies now have clear laws governing who gets the throne. In the UK, for example, the Succession to the Crown Act of 2013 made some major changes, like allowing female heirs to inherit the throne even if they have younger brothers.
But not everyone’s on board with these changes. Some traditionalists argue that altering centuries-old rules undermines the very essence of monarchy. Others say it’s time to modernize and reflect the values of today’s society. So, where do we draw the line?
Common Rules Across Monarchies
- Primogeniture: The firstborn child inherits the throne.
- Religious requirements: Many countries require monarchs to follow a specific faith.
- Marriage restrictions: In some cases, marrying outside a certain religion or family can disqualify someone from the line of succession.
Famous Succession Disputes
Let’s be real: royal families aren’t immune to drama. Throughout history, there have been plenty of succession disputes that turned into full-blown scandals—or even wars. Here are a few of the most famous ones:
The War of the Roses: England’s 15th-century battle for the throne between the Houses of Lancaster and York. Spoiler: the Tudors eventually won.
Henry VIII’s Divorces: When the King of England wanted to annul his marriage to Catherine of Aragon, it sparked a religious and political crisis that ultimately led to the English Reformation.
The Jacobite Rebellions: A series of uprisings in Scotland and England in the 17th and 18th centuries aimed at restoring the Stuart dynasty to the throne.
Lessons Learned from Succession Disputes
One thing’s for sure: when it comes to crown family succession, clarity is key. Ambiguity or favoritism can lead to conflict, so having clear, written rules is essential. And while disputes may seem like ancient history, they still have relevance today—especially in countries where succession laws are still evolving.
Gender and Succession: The Evolution
For centuries, crown family succession was heavily biased toward men. The idea that a woman couldn’t handle the responsibilities of monarchy was deeply ingrained in many cultures. But times have changed, and so have the rules.
In recent years, several countries have updated their succession laws to allow for equal rights between male and female heirs. Sweden, for example, became the first country to implement absolute primogeniture in 1980, meaning the eldest child—regardless of gender—inherits the throne.
Challenges to Gender Equality in Succession
Despite progress, there are still challenges to achieving true gender equality in crown family succession. Some traditionalists argue that changing the rules undermines the historical integrity of the monarchy. Others worry about the potential impact on national identity and cultural heritage.
Religious Factors in Succession
Religion has long played a role in crown family succession, especially in countries with established state religions. In the UK, for instance, the monarch must be a member of the Church of England. This requirement dates back to the Act of Settlement in 1701 and remains in place today.
But as societies become more diverse, questions about the role of religion in succession are becoming more pressing. Should monarchies continue to prioritize one faith over others? Or is it time to rethink these ancient rules?
Religious Requirements Around the World
- UK: Monarchs must be Protestant and cannot marry a Catholic.
- Japan: The Emperor must be a member of the Shinto faith.
- Sweden: The monarch must be a member of the Church of Sweden.
How Different Countries Handle Succession
Not all monarchies handle crown family succession the same way. In some countries, the process is highly formalized, with strict rules and regulations. In others, it’s more flexible—or even non-existent. Let’s take a look at how a few different countries approach this important issue.
United Kingdom: The UK has a well-established system of succession based on primogeniture and religious requirements. The line of succession is clearly defined, and changes to the rules must be approved by Parliament.
Japan: Japan’s Imperial House Law dictates that only male heirs can inherit the throne. However, recent debates have raised questions about whether this rule should be updated to allow for female succession.
Sweden: Sweden practices absolute primogeniture, meaning the eldest child—whether male or female—inherits the throne. This change was made in 1980, making Sweden a trailblazer in gender equality in succession.
Unique Succession Practices
Some countries have truly unique approaches to crown family succession. For example, in Bhutan, the king consults with a group of senior officials before naming his successor. In Saudi Arabia, the throne is passed among the sons of the founding king, rather than following a strict line of primogeniture.
The Role of Parliament in Succession
In many countries, Parliament plays a key role in determining the rules of crown family succession. In the UK, for example, changes to the succession laws must be approved by both the House of Commons and the House of Lords. This ensures that the process remains transparent and accountable to the public.
But what happens when Parliament and the monarchy disagree? In rare cases, this can lead to tension—or even conflict. The key is finding a balance between preserving tradition and adapting to modern values.
How Parliament Shapes Succession Laws
Parliament can influence crown family succession in several ways:
- Amending existing laws to reflect changing societal values.
- Approving or rejecting proposed changes to the rules of succession.
- Ensuring that the process remains fair and transparent.
The Future of Crown Succession
So, what does the future hold for crown family succession? As societies continue to evolve, it’s likely that we’ll see more changes to the rules governing royal lineages. Gender equality, religious diversity, and even environmental concerns could all play a role in shaping the future of monarchy.
But one thing’s for sure: crown family succession will always be a fascinating topic. Whether you’re a history buff, a fan of royal dramas, or just curious about how these systems work, there’s something undeniably captivating about the world of kings, queens, and thrones.
Predictions for the Future
Here are a few predictions for the future of crown family succession:
- More countries will adopt absolute primogeniture to promote gender equality.
- Religious requirements may become less strict as societies become more secular.
- Monarchies may face increasing pressure to adapt to modern values and global challenges.
Conclusion: Why Crown Succession Still Matters Today
Crown family succession might seem like an ancient concept, but it’s still highly relevant in today’s world. From shaping national identity to influencing global politics, the way monarchies transition power can have far-reaching effects. So, whether you’re fascinated by the history or curious about the future, there’s no denying the importance of understanding this complex and often controversial process.
Now it’s your turn. Do you think crown family succession needs to change? Or are the old rules still relevant in today’s world? Leave a comment below and let us know what you think. And if you enjoyed this article, don’t forget to share it with your friends and check out our other posts on all things royal!


Detail Author:
- Name : Carmen Kohler
- Email : raleigh06@donnelly.com
- Birthdate : 1975-07-25
- Address : 357 Upton Wall Suite 390 Camryntown, AK 72787
- Phone : +1-916-712-0744
- Company : Romaguera PLC
- Job : Air Traffic Controller
- Bio : Molestiae dignissimos consectetur sequi inventore qui dolor. Ut fugiat odio magni id omnis eos quis accusamus. Laborum voluptatem voluptas pariatur tenetur.